Broader Impact Highlights
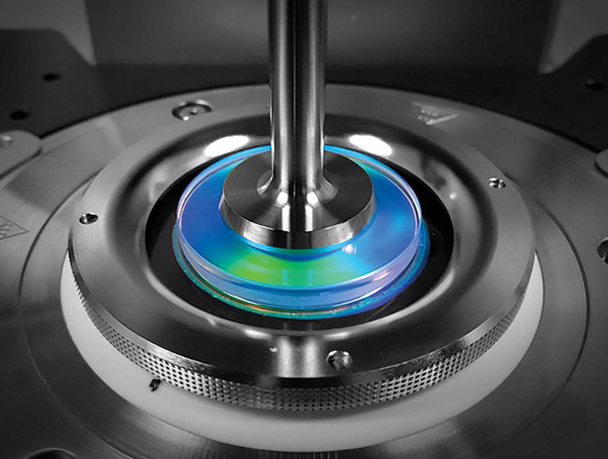

Color, Structure, and Rheology of a Bottlebrush Copolymer Solution
A combination of high-end microscopy, rheology, and neutron scattering was used to show how the shear rate alters the structure and color of these bottlebrush polymer
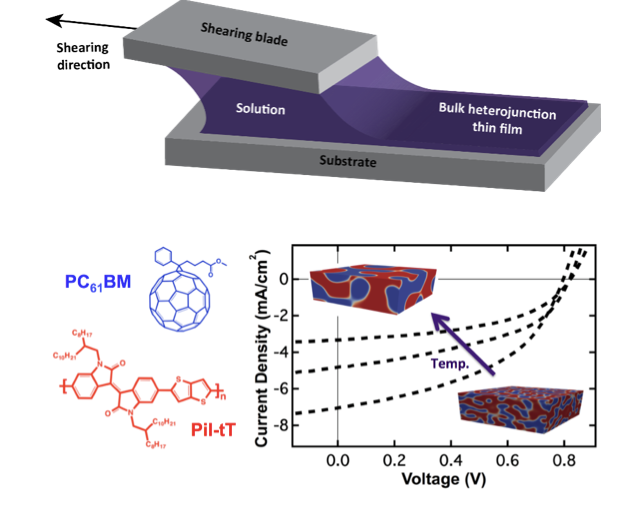
Tuning Organic Solar Cell Domain Properties
Zhenan Bao, Michael Toney
Despite having achieved the long sought-after performance of 10% power conversion efficiency, high performance organic solar cells are still constrained to small devices fabricated by spin coating. Efforts to scale up via printing lag considerably behind, revealing an extreme sensitivity to different fabrication methods.
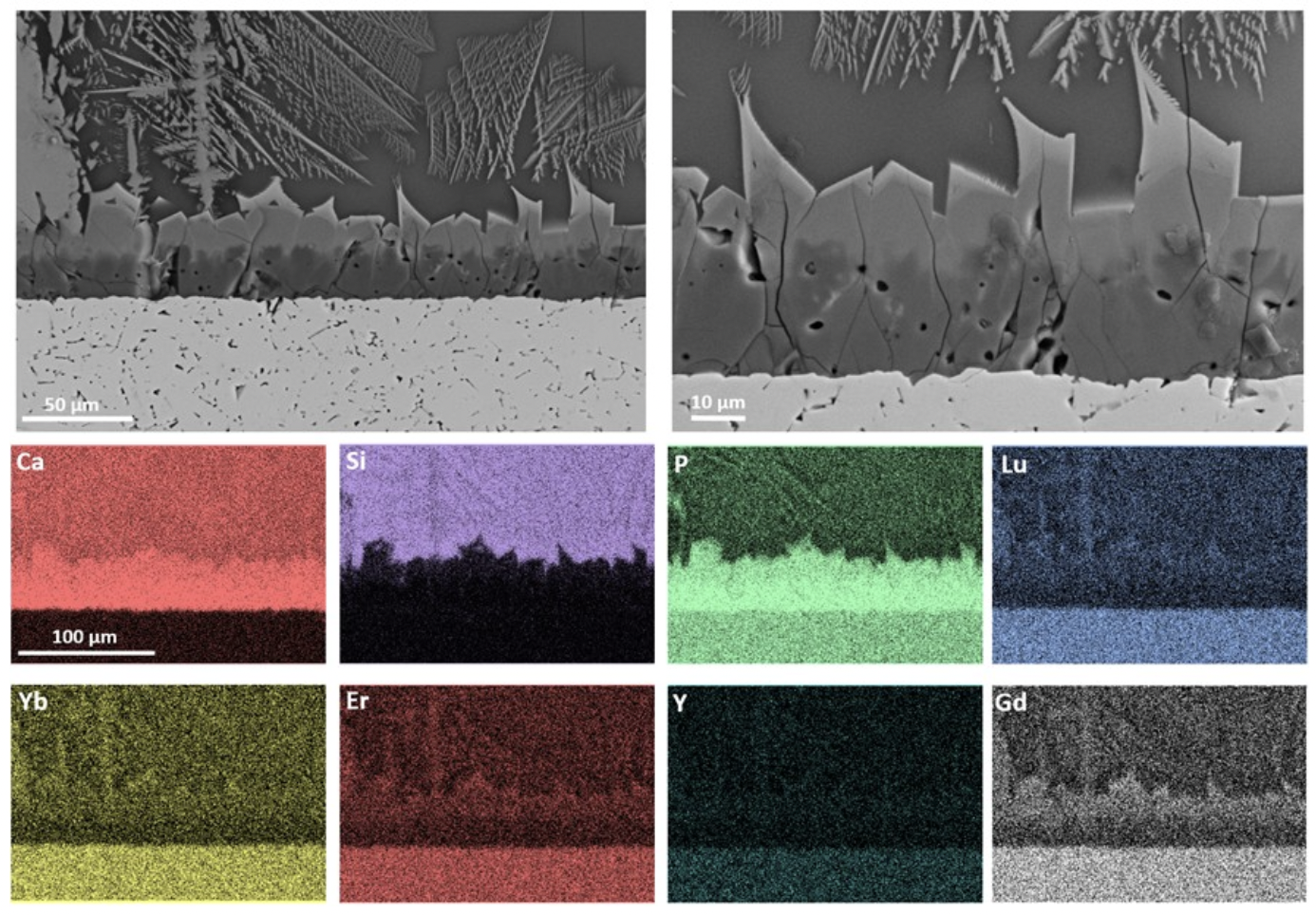
Machine Learning Accelerated Design and Discovery of Rare-earth Phosphates as Next Generation Environmental Barrier Coatings
Researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute synthesized single phase multiple component rare-earth phosphate as potential environmental barrier coatings of structure materials for space and aerospace application.
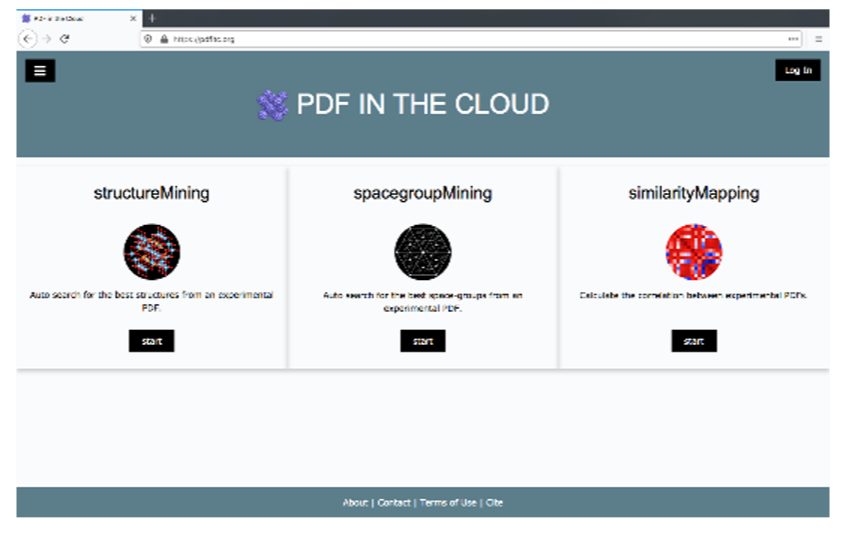
An AI-driven, Cloud-based, Materials Discovery Platform for Nanomaterial Structure: PDFitc
S. Billinge, Q. Du, D. Hsu (Columbia U.)
We have developed a cloud-based, AI driven, platform for nanomaterial structure determination: “PDF in the cloud” (PDFitc.org), which consists of various applications for nanostructure determination, including a ML-based classifier for discovering material symmetry from a measured dataset, a high-throughput structure screening tool for predicting the structure of a measured signal, and a data-similarity visualization tool for finding changes in a signal in a time or temperature series.
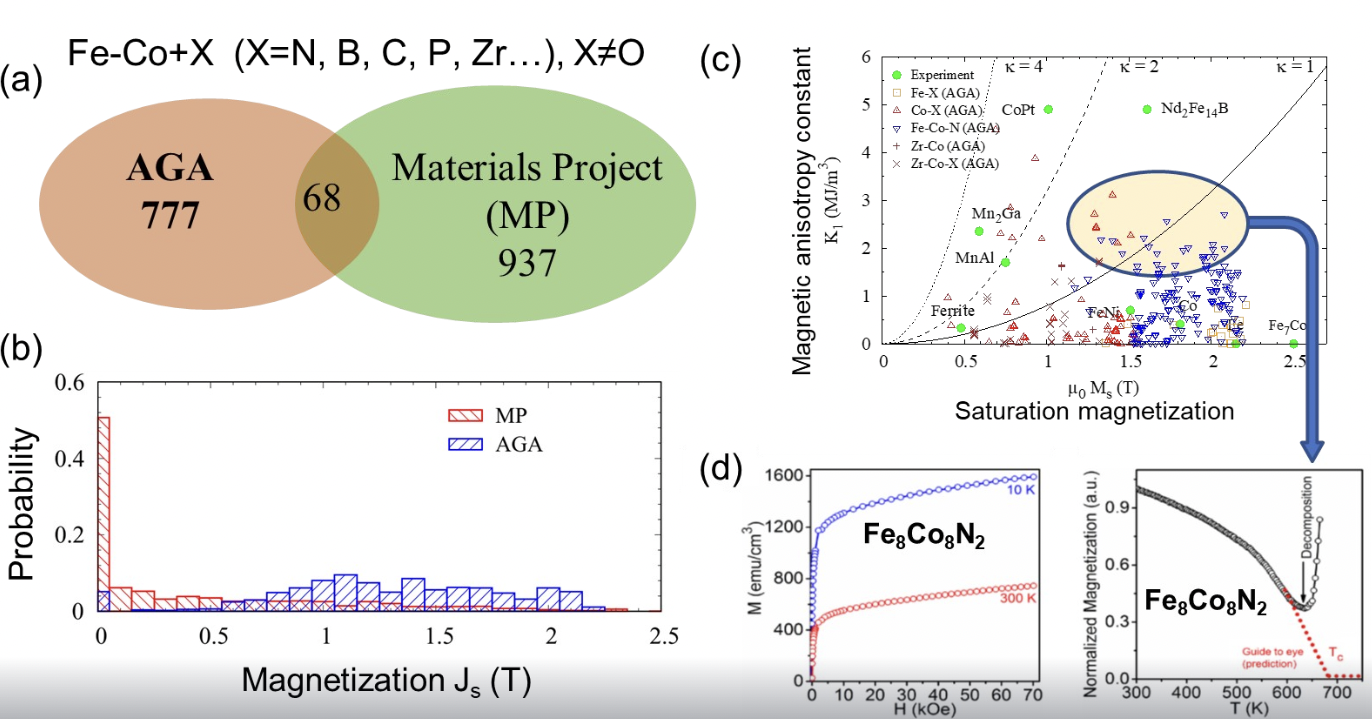
Discovering Rare-earth-free Magnetic Materials
J. Chelikowsky , K. Ho, C. Wang, D. Sellmyer, X. Xu
An open-access database is designed to facilitate machine learning.
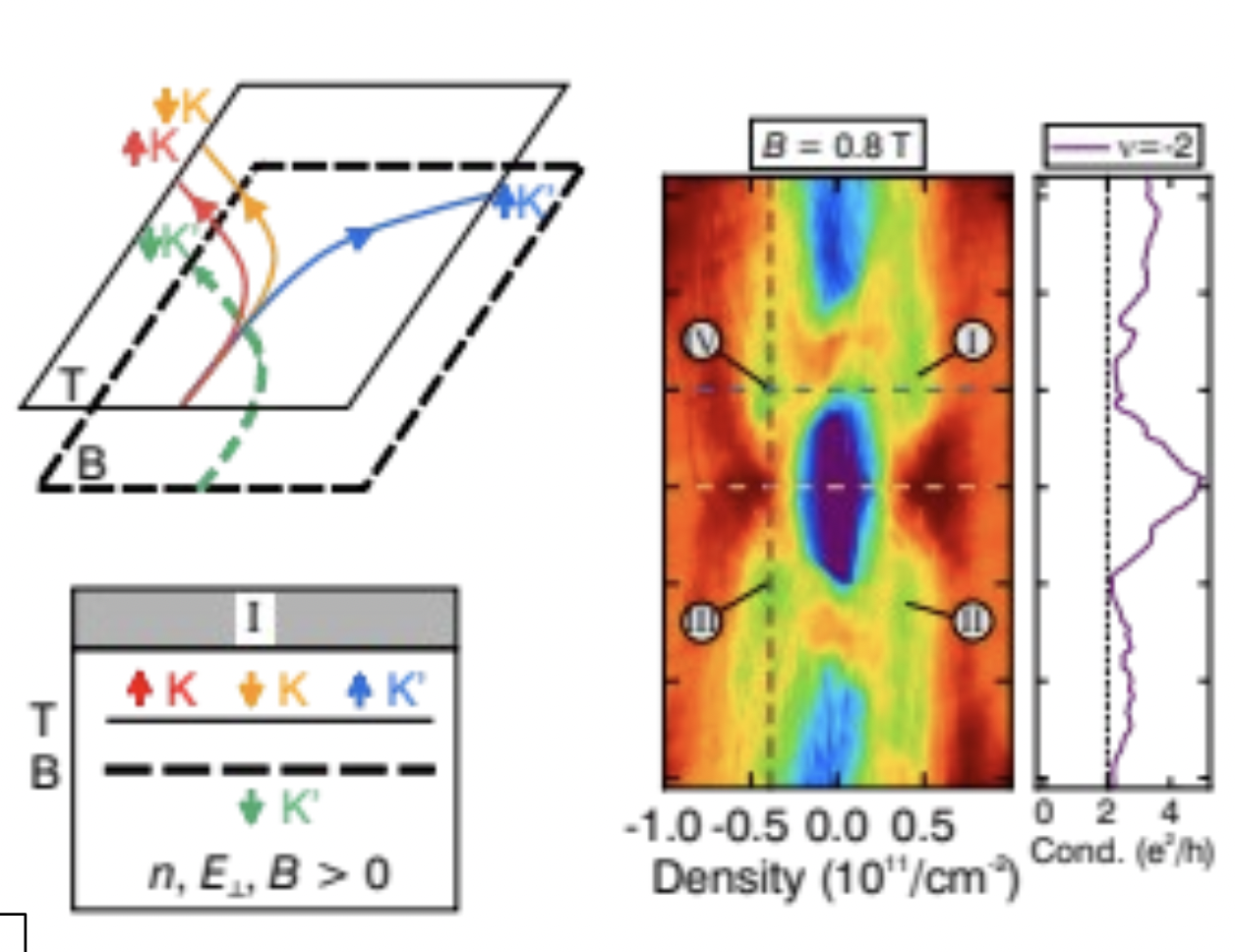
Discovery of Tunable Quantum Anomalous Hall Octet
Fan Zhang (University of Texas at Dallas)
Bernal bilayer graphene is a naturally occurring system with neither spin-orbit coupling nor moiré complex. •Quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) octet, i.e., eight states exhibiting quantum Hall effect at zero magnetic field, was theoretically predicted and experimentally observed.
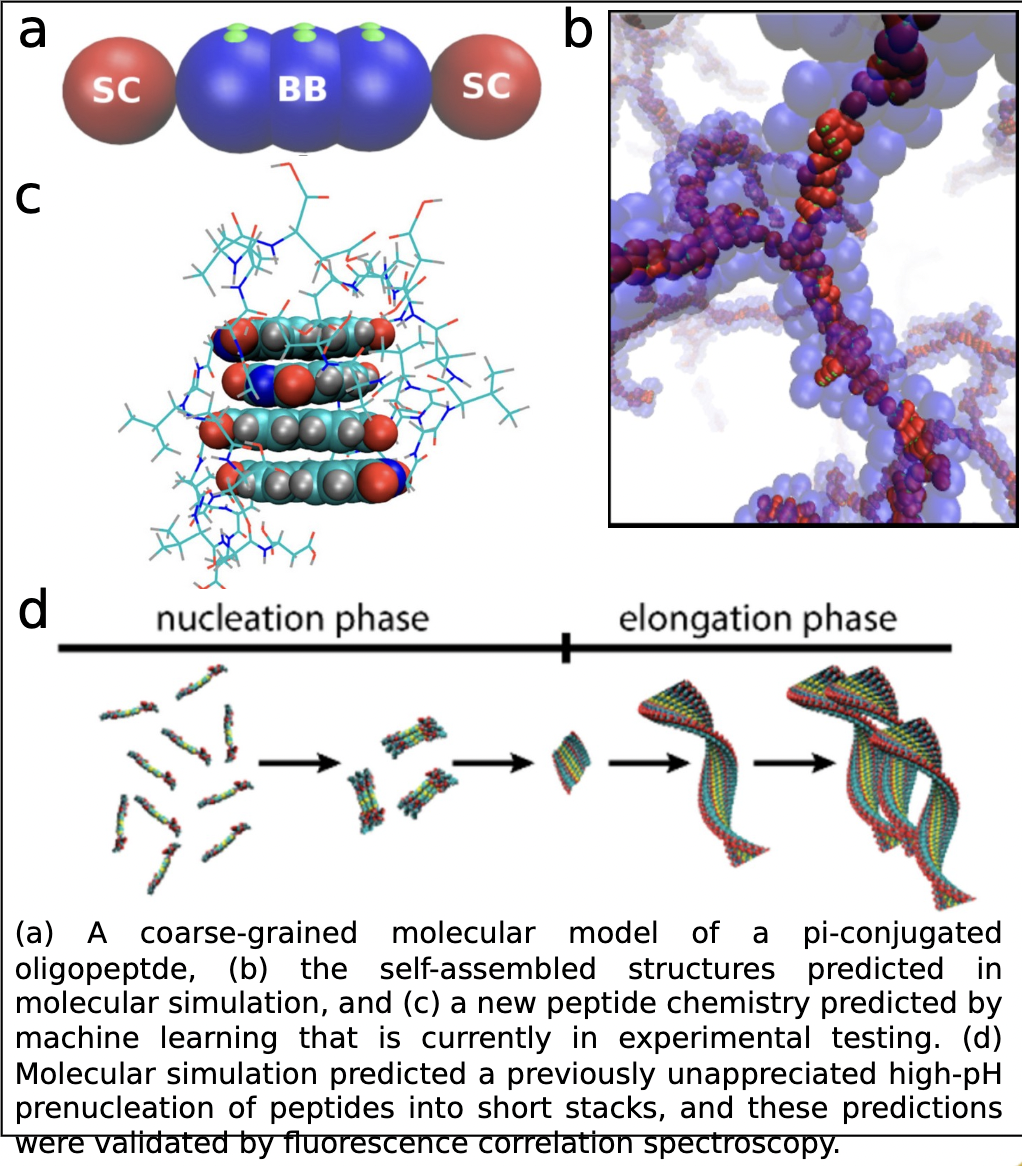
Self-assembled Peptide-p-electron Supramolecular Polymers
A. Ferguson
Non-natural peptides containing electron-rich aromatic subunits have demonstrated the remarkable ability to spontaneously assemble into long fibers with optical and electronic responses similar to conventional silicon electronics. These molecules have the potential to serve as new biocompatible organic electronics with uses in medical interventions and clean energy.
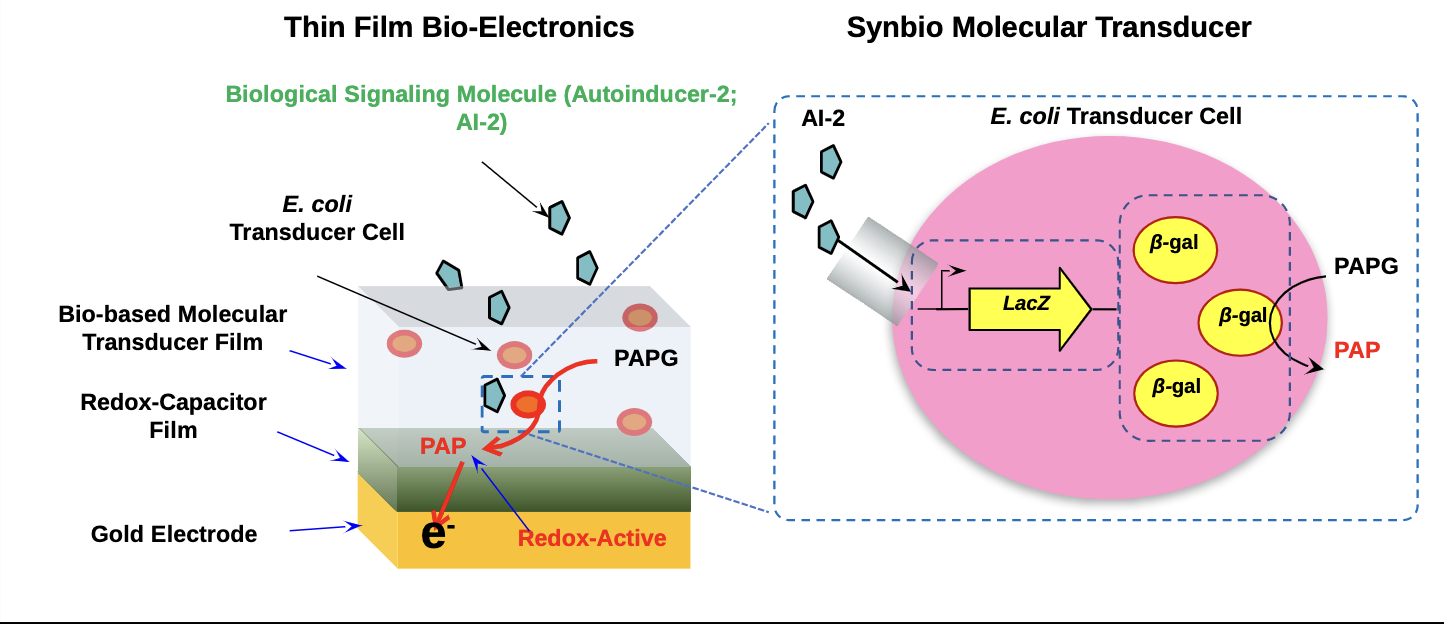
Enlisting Synbio for Molecular Communication
Gregory Payne and William Bentley
Divergent approaches to process information: •Electronics use electrons •Biology uses ions & molecules

A New Paradigm for Accessing Chemical Information
Gregory Payne and William Bentley
In the 1960s work began toward the personal computer – a landmark in information processing. Since then, devices to access and analyze information have become smaller, faster, cheaper, easier to use and more powerful.
Charge Disproportionation and Complex Magnetism in a PbMnO3Perovskite Synthesized under High Pressure
Jianshi Zhou (University of Texas-Austin)
Because of the possible crossover of Pb and 3d transition-metal (TM) redox levels, a charge transfer between Pb and TM leads to a continuous evolution from Pb2+Ti4+O3 to Pb4+Ni2+O3 in the perovskite family of PbTMO3.
Showing 61 to 70 of 120